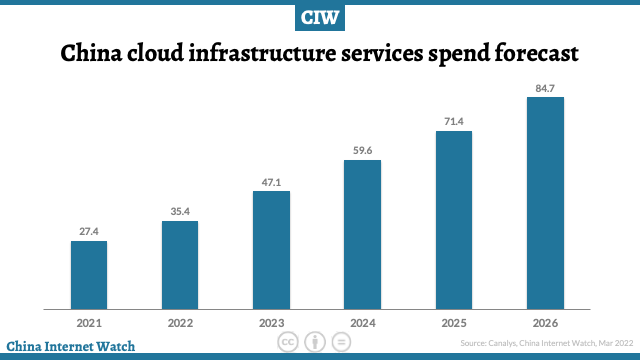
The fourth quarter of 2021 saw a year-on-year increase of 33% to US$7.7 billion. Canalys predicts that by 2026, the scale of the cloud infrastructure market in the mainland will reach US$85 billion, and the five-year compound annual growth rate will be 25%.
Visit here for AI Cloud market share.
Alibaba Cloud remains the leader with a 37% market share, ranking first in the cloud market in 2021, Huawei Cloud and Tencent Cloud second and third respectively, and Baidu AI cloud fourth. In 2021, the four cloud providers jointly accounted for 80% of the market share.
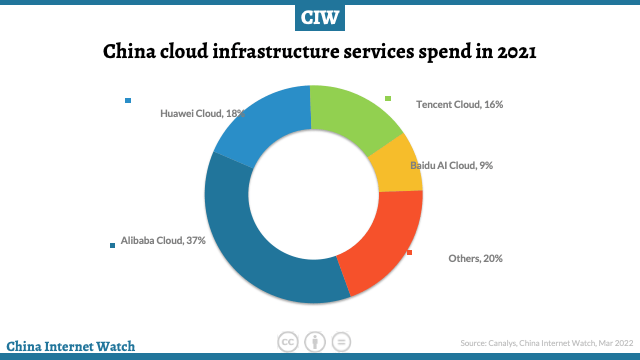
Huawei Cloud reached an 18% market share in 2021, with an annual growth of 67%. The rapid growth has widened the gap between Huawei cloud and Tencent Cloud, ranking second in the market.
Tencent cloud, the third-largest provider, accounted for 16% of the market share, an increase of 55%. Tencent Cloud grew steadily as a whole in 2021, with diversified growth in multiple sectors.
Baidu AI Cloud, the fourth-largest vendor, accounted for 9% of the market share, an increase of 55%.
Top 10 forecasts for China cloud computing market 2021-2024
China’s Public Cloud Services Market to Grow to 10.5% of global share by 2024
In 2020, the overall market size of global public cloud services (IAAs/PAAS/SaaS) reached US$312.42 billion, with a year-on-year growth of 24.1%, according to IDC.
The overall market size of China’s public cloud services reached US$19.38 billion, with a year-on-year growth of 49.7%, with the highest growth rate in all regions of the world. IDC predicts that the global share of China’s public cloud service market will increase from 6.5% in 2020 to more than 10.5% by 2024.
Check out market share of IaaS and PaaS markets in China here.
CIW Subscribers (Annual) can download the chart here to see the comparison of the cloud platforms in China.
Download China Internet Overview whitepaper here.
]]>From the IaaS + PaaS market perspective, the first half of 2021 increased by 43% (vs. 48.6% in H1) year-on-year, down 6% from the first half of 2021, but still maintained the highest growth rate in the world.
In the next five years, China’s public cloud market will continue to grow at a compound growth rate of 30.9%. By 2026, the market is expected to reach US$105.76 billion, and the global share of China’s public cloud service market will increase from 6.7% in 2021 to 9.9%.
The competition in China’s cloud computing extends from focusing on infrastructure to the competition of comprehensive cloud platform capabilities. In addition to increasing investment in infrastructure construction at the IaaS layer, cloud vendors also continue to strengthen chip self-research capability, improve PaaS capability (data processing capability, cloud-native, low code development, etc.), build leading, fast, and perfect solution service capability and implementation and delivery ecology and develop a more comprehensive cloud platform.
The digital transformation of government and enterprises has fully entered the cloud era.
In the first half of 2021, the State Council put forward decisions on deepening the integrated development of new-generation information technology and manufacturing industry and creating new advantages of the digital economy.
Also read: the latest on China’s public cloud market
Local governments and regulators have issued relevant technical specifications and application standards of cloud computing platforms, actively promoted the all-around and in-depth integration of digital technology and social development, and accelerated the application and implementation of digital technology in various industries.
Cloud computing has become the basis and hub of digital transformation. Under this background, there is a huge demand and market space for cloud services in the field of government and enterprises.
Cloud vendors have released their own cloud-native strategies to seize the opportunity from the aspects of products, partners, standard-setting, talent cultivation, and so on.
Industry digitization and low-carbon development have become the mainstream trend. In terms of themselves, cloud vendors continue to improve product energy efficiency and promote the low-carbon development of the cloud industry by investing in innovative energy-saving technologies.
In terms of industry empowerment, cloud manufacturers invest in power electronics technology and integration and innovation with digital technology, promote the development of clean energy and the digitization of traditional energy, bring digital technology to each industry, and support all walks of life to promote low-carbon development through digitization.
In both IaaS and Iaas+PaaS markets, the competition is tight. The leading vendors Alibaba Cloud, Huawei Cloud, and Tencent Cloud have firmly taken the top three positions and jointly have 60% of the market share.
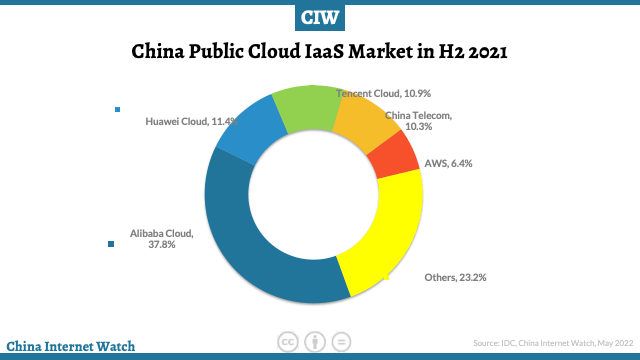
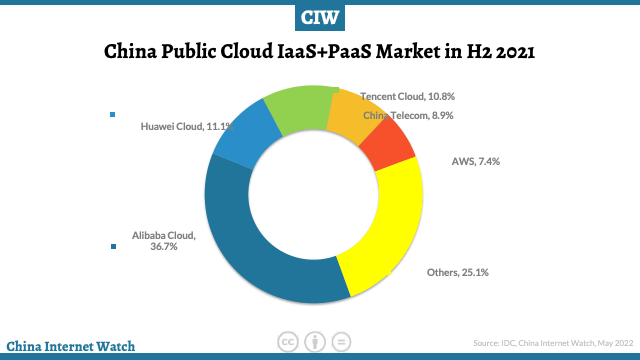
Cloud vendors in the network operator camp grew rapidly, with independent research and development and cloud network integration as their keywords.
The fourth ranked China Telecom Tianyi Cloud formed a full-stack cloud product system by the end of 2020, further deepened to the vertical industry and territory in 2021, sank the resource and service team to the local city, and the local cloud business grew rapidly, creating a new growth level for Tianyi Cloud.
Pricing only the 2nd most important in China for choosing cloud vendors
]]>Globally, the key benefits of 5G other than speed gains (e.g. network slicing, edge computing, and low-latency services) are not widely appreciated, with many companies believing 4G is ‘good enough’.
But China is a clear exception. Early partnerships and trials from local operators have paid dividends, as evidenced by the widespread intent among companies in the country’s industrial sector to utilize 5G.
Chinese operators are also leading the charge for standalone (SA) 5G, which will help deliver the key benefits of 5G for enterprises.
Awareness and knowledge of 5G are rising as hype makes way for reality.
Chinese consumers are among the most excited by the prospect of 5G. They are generally more optimistic than other markets about the benefits of 5G, with greater expectations of lower service costs, innovative services and new connected devices.
In addition, consumers in China are likely earlier adopters of 5G (versus the US, Japan, and Europe) and seem the most willing to pay more for 5G services – a key driver of potential 5G consumer revenue uplift.
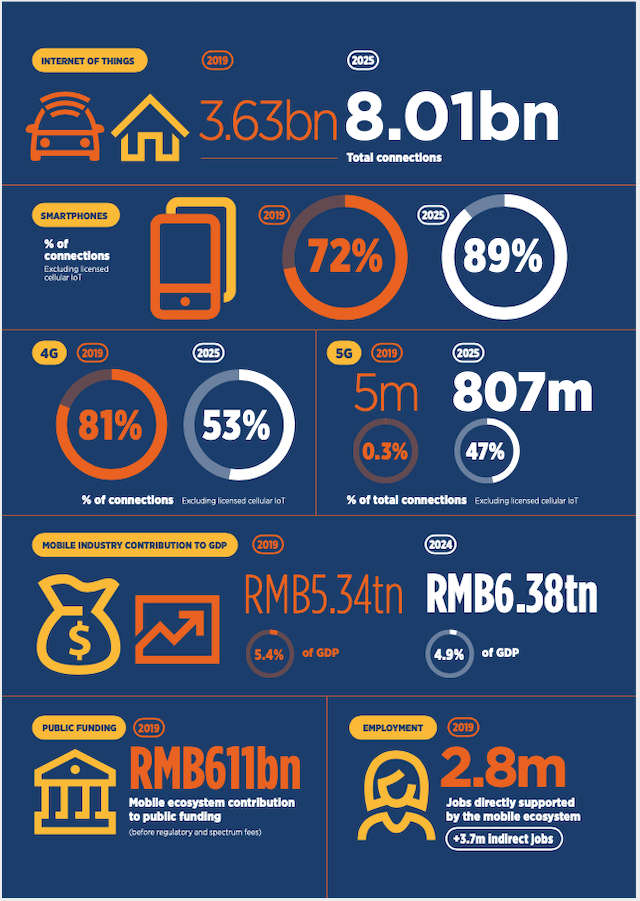
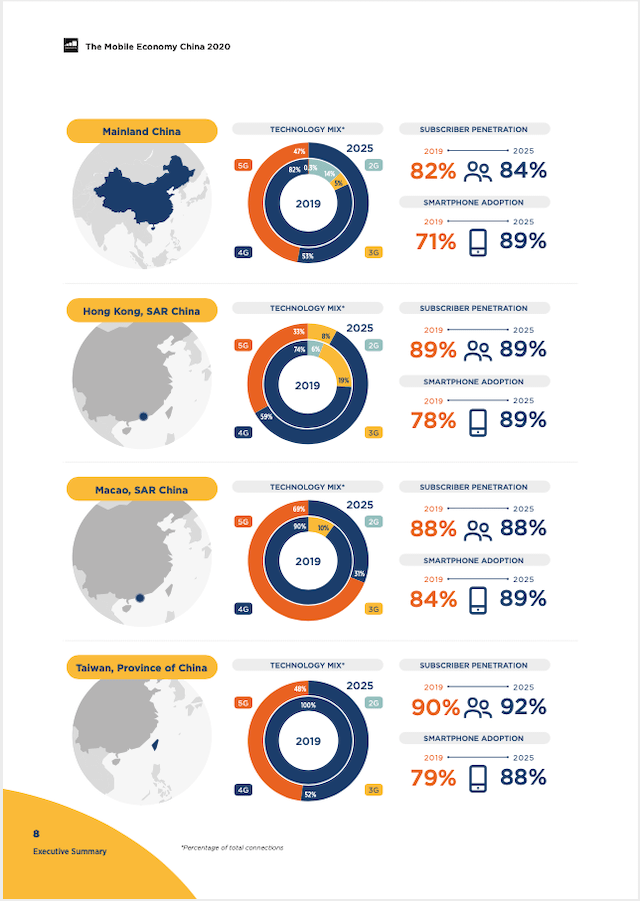
4G is by far the dominant mobile technology across China, accounting for more than 80% of total connections (excluding licensed cellular IoT). However, 4G’s share will peak in 2020 (at 82%) as 5G grows significantly.
Several 5G smartphones have been launched, many by local OEMs, and Chinese consumers are among the most keen to upgrade to 5G.
As a result, China will account for 70% of global 5G connections in 2020, and 5G adoption will grow to just under 50% by 2025, placing the country among the leading nations along with South Korea, Japan and the US.
To support this generational shift and drive consumer engagement, Chinese operators are expected to invest more than $180 billion between 2020 and 2025 in mobile capex, roughly 90% of which will be on 5G networks.
Despite some financial headwinds – including market saturation, increasing competition and the country’s ‘speed upgrade and tariff reduction’ policy – China’s mobile revenue remains stable.
Financials will recover in 2020 and 2021, and revenue will rise steadily at around 1% per year to 2025, largely because of growing revenues in enterprise IoT and new 5G services.
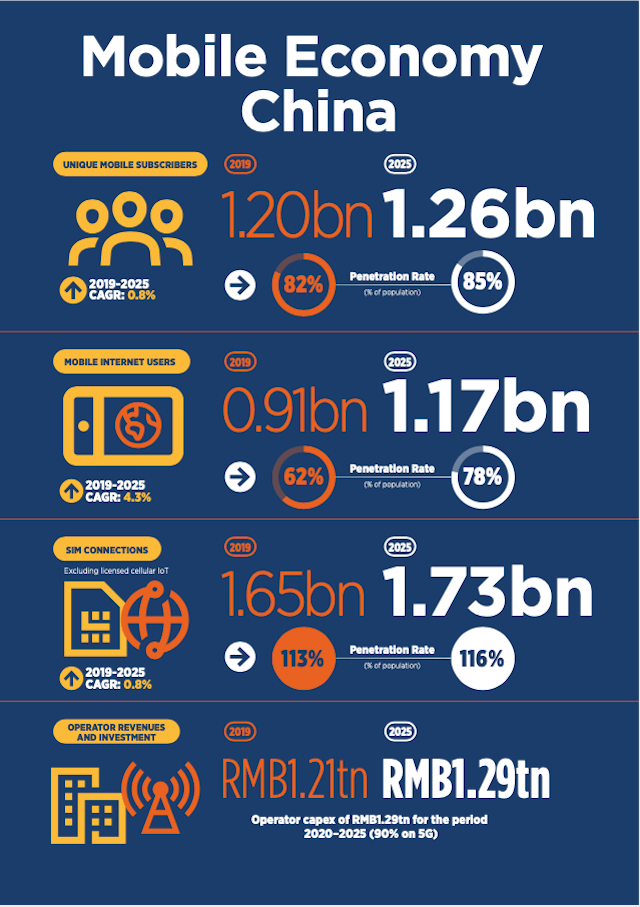
By the end of 2019, 1.2 billion people subscribed to mobile services across China.
This accounts for 82% of the region’s population and places China among the world’s most developed markets. As with all advanced markets, adding new subscribers is increasingly difficult, with the cost of reaching rural populations hard to justify against a challenging financial backdrop for operators.
Despite this, there will be around 60 million new subscribers by 2025.
Since 2012, the number of people subscribing to the mobile internet across China has doubled to more than 900 million. By 2025, nearly 260 million people will start using the mobile internet for the very first time, almost halving the unconnected proportion of the population to 22%.
Mobile continues to make a significant contribution to the Chinese economy.
In 2019, mobile technologies and services generated $759 billion of economic value added (5.4% of GDP) across China. This figure will surpass $900 billion by 2024 as the region increasingly benefits from the improvements in productivity and efficiency brought about by the increased take-up of mobile services.
Download the full report here (CIW annual subscribers) including key trends shaping the mobile industry, mobile contributing to economic growth and addressing social challenges, and policies to accelerate digital development. Subscribe here.
]]>
China’s three major telecoms operators recently released earning data for the first three quarters of 2017. China Mobile is the largest of the three and possesses obvious strengths; China Telecom is experiencing rapid growth; China Unicom has finally hurdled recent difficulties and reported an increase of 155% in net profits, but this still leaves it with profits 22 times lower than those of China Mobile.
Highlights
Regarding 4G users, China Unicom and China Telecom combined had a total of 328 million 4G network users, versus China Mobile’s 622 million; however, as of June, the former two had less than half the 4G users of the latter, suggesting that the gap is narrowing, albeit slowly.
China Telecom has a commanding lead in the broadband business, and had 131 million broadband customers at the end of September, an increase of 8.2 million. However, China Mobile’s broadband business broke 100 million users in September, an increase of 25.8 million. If it can keep up the pace of growth it may surpass China Telecom’s broadband business sometime next year.
Due to ongoing network expansions and the increased cost of tower leasing, all three operators are experiencing increasing operating expenses compared with last year; China’s Telecom’s expenses increased by 9.8%, while Unicom’s increased by 3.2%.
China Unicom’s profitability increased significantly, aided by its 2I2C strategy and strategic cooperation with Internet companies; its partnerships have allowed the two sides to complement one another, with its online partners’ big data analysis capabilities and advantages in reaching online customers helping it to extend business coverage and access its target consumers.
Traditional core businesses for mobile operators, including SMS and voice calling, are all in decline. The number of talk minutes used fell by 7.1% in the first three quarters of 2017.
Improving performance
China Mobile’s revenue for the first three quarters was up 4.9% to 569.5 billion yuan. Profit attributable to shareholders was 92.1 billion yuan, an increase of 4.6% over the same period in 2016.
China Telecom’s revenue for the first three quarters was up 4.1% to 274.7 billion yuan. Profit attributable to shareholders was 18.5 billion yuan, an increase of 45.5% over the same period in 2016.
China Unicom’s revenue for the first three quarters fell by 1.4 billion yuan to 201.7 billion yuan. Profit attributable to shareholders was 4.05 billion yuan, an increase of 155.3% over the same period in 2016.
Overall, all three companies performed well thus far in 2017; Telecom grew by the largest amount, Mobile maintained its status as the largest service provider, and Unicom, though revenue receipts fell, vastly increased its profitability. China Unicom’s income from its mobile business increased by 6.7% to 117 billion yuan; analysts believe this growth and recovery is contingent on increasing its 2I2C, 2B2C, and other online sales initiatives while maintaining low-cost, low-subsidy user acquisition.
Unicom’s businesses “under attack from all sides”
Thus far, China Unicom and China Telecom’s 4G businesses have been living in the shadow of China Mobile’s. However, their latest reports show that the former two reached a total of 328 million 4G users, 34.5% of the market, in 2017. In 2016 they had a combined market share of 29%; in 2015 the corresponding figure was 10%. Thus, they are gradually eroding China Mobile’s lead.
China Telecom was formerly a strong second within the 4G market, but this past year China Unicom has nearly caught up on the backs of an increase of 55.73 million users (vs. Telecom’s 45.65 million). It now has a user base only 8 million larger than China Unicom, with 168 million users in all.
In addition, its broadband business is under assault by China Unicom, which at 100 million users has nearly caught up to Telecom’s 131 million users and may overtake it next year if its rapid growth continues. China Telecom’s advantages in both businesses are no longer obvious.
Strategies and Comments
China Mobile maintains an absolute lead in its mobile and 4G businesses. It has said that it will maintain its “four-wheel drive” integration strategy and work to develop the personal, family, commercial, and new services markets to maintain growth.
China Telecom believes that by promoting business transformation it will enhance its advantages in the future. It also intends to break through institutional barriers to productivity, and strengthen its initiative in the areas of implementation and management.
China Unicom stressed innovation and integrated development and plans to accelerate the recovery of its broadband business while accelerating the transformation of the internet to enhance productivity. It intends to embrace market-oriented reforms to improve efficiency and direct its efforts. It expected the fourth quarter to be challenging as it will abolish domestic roaming fees.
China smartphone market in Q3 2017; 4 out of 10 using Huawei or iPhone
]]>
By the end of Q2 2015, the penetration rate of smartphones has reached 65.5% in China urban regions, an increase of 4.3% compared with the previous quarter and an increase of 18.9% year over year. The penetration rate of China Mobile smartphone users was the highest which reached 66.3% according to Kantar Worldpanel ComTech.
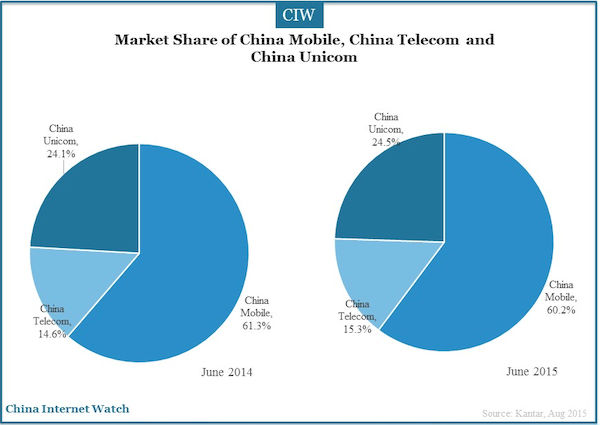
Although the ratio of China Mobile users was 1.1 percentage points lower year on year, it still accounted for 60.2% market share, more than the total number of users of the other two telcom networks combined.
Users who chose not to use China Mobile any more were mainly the female, post-00s and post-90s, 3G network users, post-paid subscribers in third-tier and fourth-tier cities. More than half of the lost users joined the network of China Unicom, mainly due to the recommendation of their friends and relatives. New users who chose to use China Mobile were mainly because of the mobile 4G network, while many users complained about the cost-effectiveness and the imparity clauses.
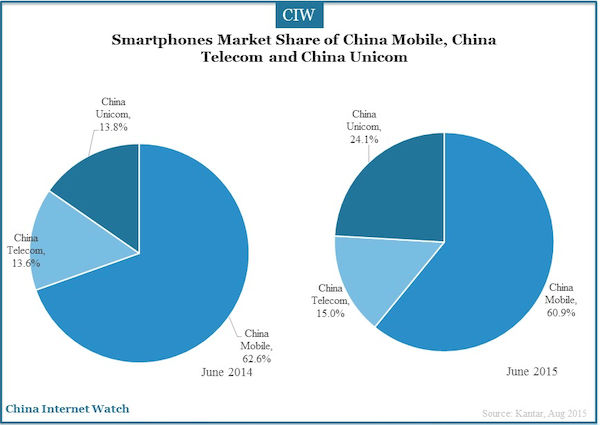
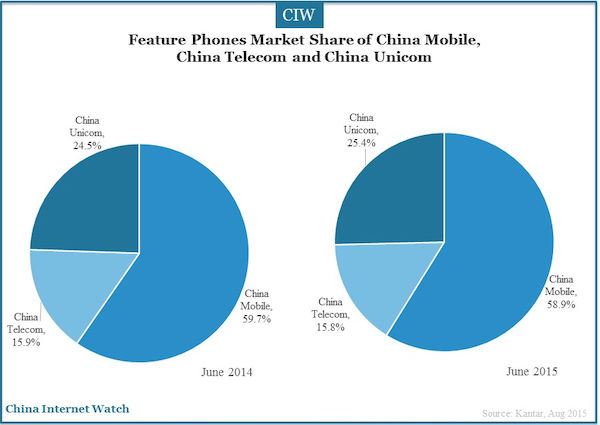
In contrast, the number of China Telecom mobile phone users continued to grow, which reached 15.3%. Home broadband, landline telephone and other services helped China Telecom in the growth. In addition, there were a considerable number of users who chose China Telecom mobile phones for its favorable price.
In order to avoid the loss of more users, China Mobile should encourage users to upgrade to the 4G network.
]]>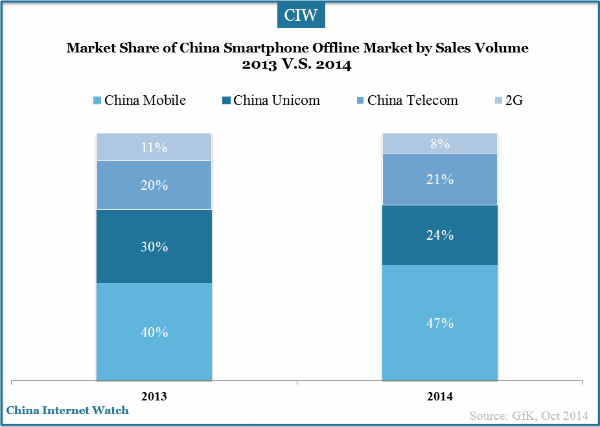
In China smartphone offline market by sales volume, China Mobile market share rose to 47% in 2014 while China Unicom dropped to 24%. China Telecom’s market share had little change from 2013 according to a research from GfK. Besides, 2G is becoming less popular in China as its market share decreased to 8% in 2014.
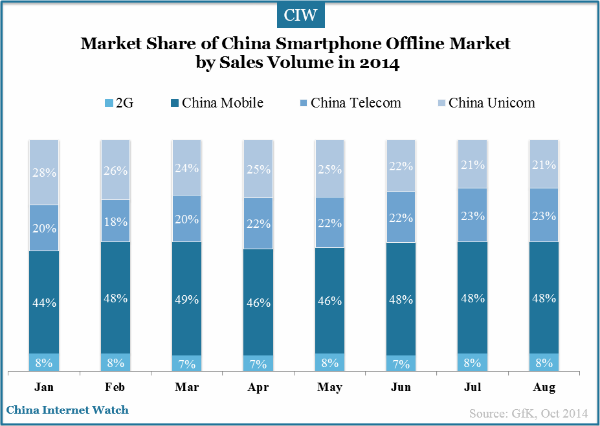
China Mobile has increased more investment in 4G smartphone market since last year, which contributes to its rapid development in China smartphone offline market in 2014. In the first half of 2014, total sales of smartphones in China have exceeded 185.563 million units according to data from iiMedia Research. 3G Smartphone accounted for 72% of all the phones sold and the market has higher demand on 4G smartphones as 4G network is heavily promoted by the telcos in China.
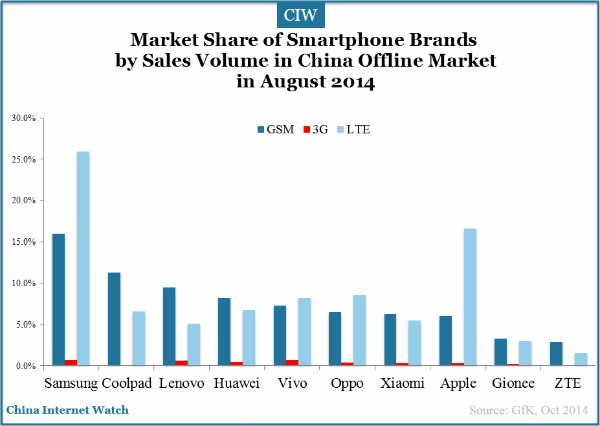
The market share of Samsung, Lenovo and Apple decreased in August 2014 in China’s smartphone offline market, while Vivo, Huawei, Oppo and Xiaomi all have increased market share.
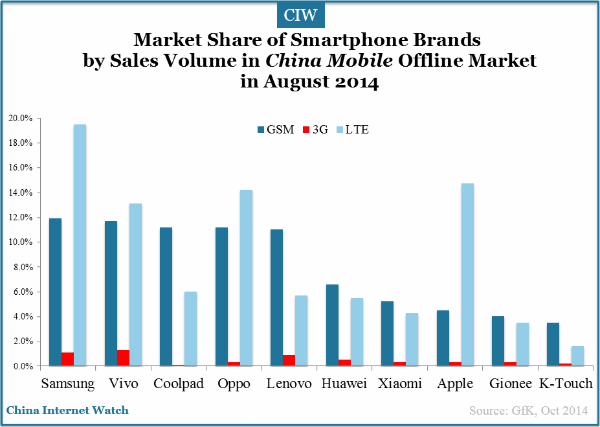
In August 2014, top 5 smartphone brands by market share in China Mobile offline market were Samsung, Vivo, Goolpad, Oppo and Lenovo.
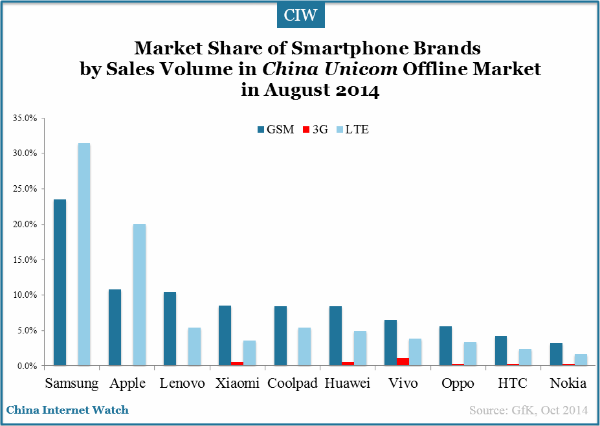
The top 5 smartphone brands by market share in China Unicom‘s offline sales channels were Samsung, Apple, Lenovo, Xiaomi and Coolpad.
Also read: Samsung and Xiaomi Ahead of Apple, Leading China Smartphone Market
]]>
iPhone6 and iPhone6 Plus finally got network access license from China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology on 30 September in 2014. Apple also announced that new iPhones will be available for consumers to buy in mainland China on 17 Oct 2014.
In addition to Apple online and retail store, iPhones’ selling channels have been extended. Three operators including China Mobile, China Unicom and China Telecom, now all provide ordering service. Total orders exceeded 4 million through channels like three telco operators and virtual operators such as Suning, D.Phone, Jingdong and others.
Announcement on China Mobile’s official website now is written: “Users can book iPhone 6 & iPhone 6 Plus on www.10086.cn, 10086 web portal, Wechat platform, JD and by dialing 10085.
China Unicom and China Telecom both provide iPhone 6 and Plus with all netcom version. However, they do not provide bare iPhones booking now.
Within 6 hours in China, three operators received over 1 million bookings and bookings for 64GB version are much more than other ones.
iPhone 6 and Plus orders on JD.com needs users provide their real names, e-mail address and telephone numbers to be informed of available time. Virtual operator, Suning also made promotion for new iPhones orders.
In China, need for iPhone 6 and iPhone 6 Plus is much higher than before. It’s really a pleasure for Chinese to experience new iPhones and a potentially huge sales success in China for Apple.
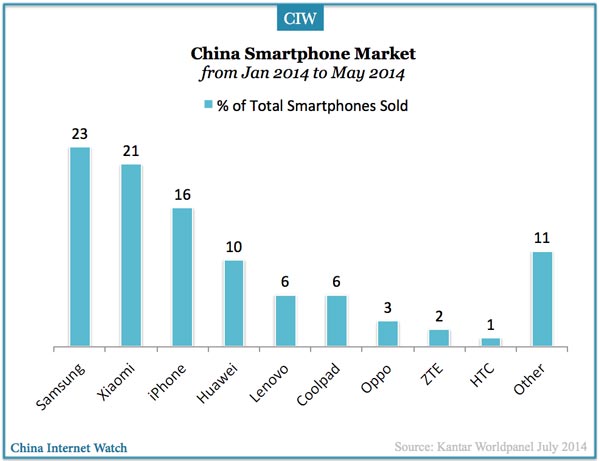
Samsung leads China’s smartphone market (23%) by total sales volume, followed by Xiaomi (21%) and iPhone (16%) during a five-month period ended in May 2014, reported by Kantar Worldpanel:
The number of Smartphone users in China has exceeded 556 million by June 2014 in China, an increase of 4.5% from the prior quarter; more on China mobile market in H1 here.
Also read: Huawei, Lenovo the World’s 3rd and 4th Largest Smartphone Vendor in Q2 2014
]]>
In July 2014, total number of subscribers has exceeded 296 million in China Unicom’s mobile services business, with a monthly increase of 888 thousand new subscribers according to the released data from China Unicom for July.
In terms of fixed-line broadband, the number of subscribers reached 67.798 million with 378 thousand new subscribers while the number of local telephone subscribers was 85.44 million with a decrease of 631 thousand according to data from China Unicom.

By June 2014, the number of 4G subscribers in China had exceeded 13.97 million according to Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT). China Mobile took advantage of 4G trend and gained 5.834 million new 4G subscribers and to a total number of 13.943 million subscribers. China Mobile now has 99.8% of all the 4G subscribers in China.
China Mobile has 241 million 3G subscribers and 20.437 million 4G subscribers according to China Mobile’s official data.
At the end of last year, MIIT issued 4G license based on TD-LTE technology to the three telcos in China though China Unicom and China Telecom preferred FDD-LTE. In June, MIIT granted China Unicom and China Telecom with licenses with network compatible for TD-LTE and FDD-LTE.
Read more: China to be the biggest 4G market in 2019
]]>
According to a piece of public information on Fuzhou City government website, Apple started using China Telecom cloud storage for iCloud data from China users on 8 August 2014 after fifteen months’ testing.
The same document reveals that the downtime of the used China Telecom data center is 4 minutes and 19 seconds.
iCloud is the latest branding of Apple’s cloud computing services. It has previously been branded as iTools in 2000, .Mac in 2002, and MobileMe in 2008.
]]>
Wall ads in rural areas prove to be a good way of penetrating into lower tier cities; let’s take a look at some of the wall ads of China internet companies.








On December 4 2013, China issued 4G licenses to China Mobile, China Unicom and China Telecom at the same time. The three telecom enterprises were given 4G TD-LTE operating permission.
Ericsson’s recent mobile market report forecast that China would be the biggest 4G LTE market in 2019, with over 700 million 4G LTE users. Meanwhile, Ericsson announced their support in China Mobile to build the world largest 4g LTE network.
4G LTE is the fastest developing mobile telecom technology in the history. Because of its high internet access speed and stability, flexibility, LTE becomes the indispensable network infrastructure.
]]>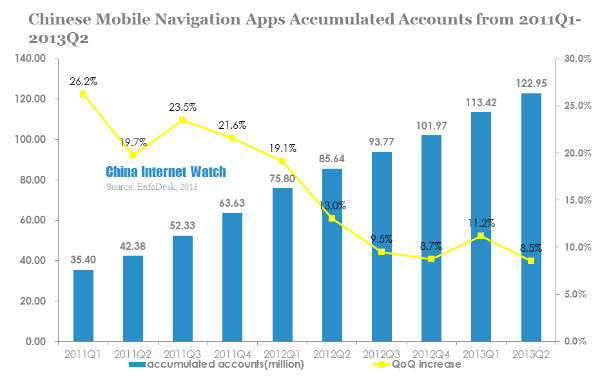
Enfodesk released its report on China LBS market, by the end of 2013 Q2, China mobile navigation apps accounts reached 120 million, with a QoQ increase of 8.5% and a YoY increase of 43.6%.
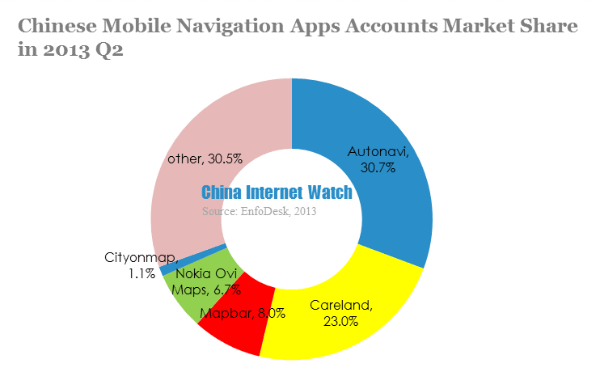
Autonavi, Careland and Mapbar were the top three navigation apps in 2013 Q2.
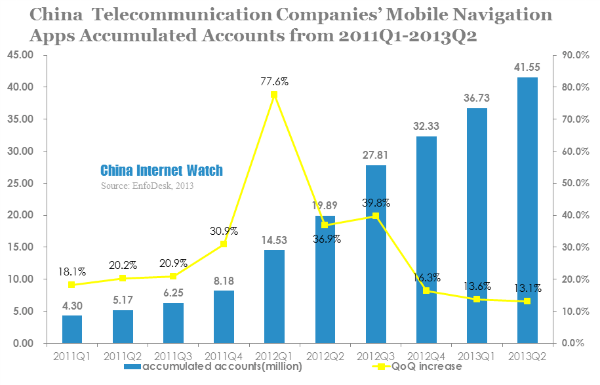
By the end of June 2013, China telecommunication companies’ mobile navigation apps accumulated accounts reached 41.55 million, with a QoQ increase of 13.1% and a YoY increase of 108.9%.
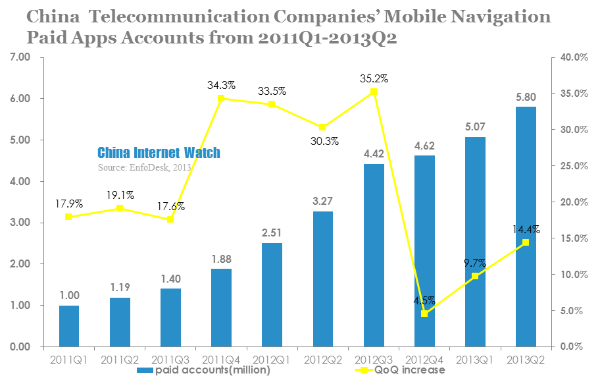
In 2013 Q2, China telecommunication companies’ mobile navigation apps paid accounts reached 5.8 million, with a QoQ increase of 14.4%. Paid accounts occupied 14% of total navigation app users.
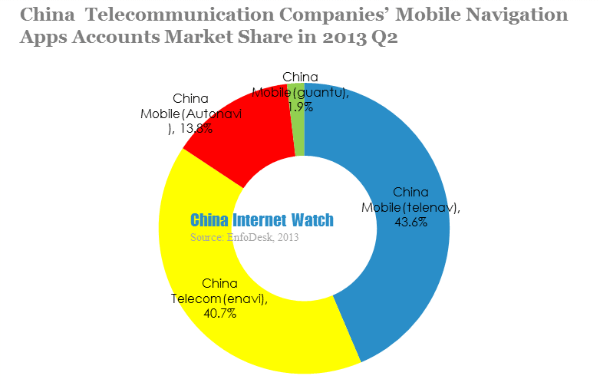
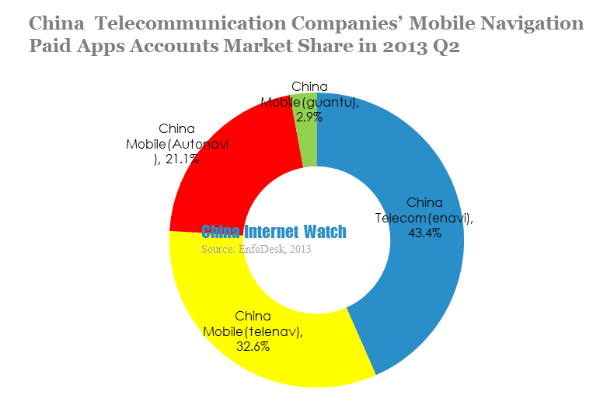
In 2013 Q2, both China Telecom’s enavi app accumulated accounts and paid accounts grew quite a lot.
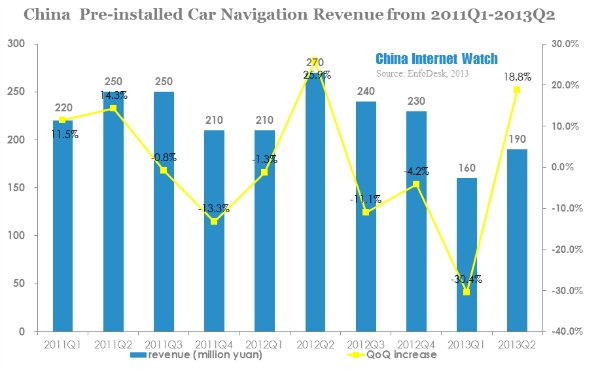
In 2013 Q2, China pre-installed car navigation market revenue was 190 million yuan (USD 31 million), with a QoQ increase of 18.8% and a YoY drop of 29.6%.
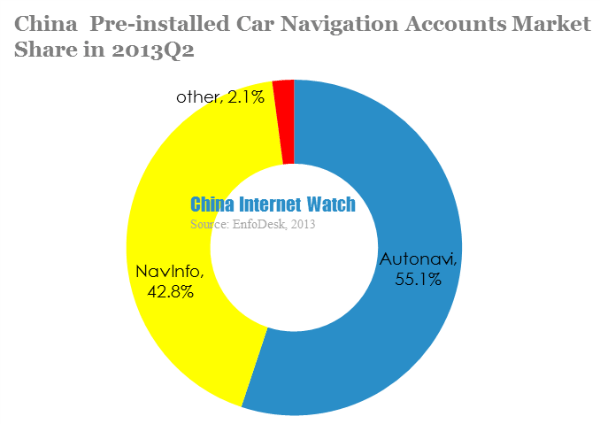
Autonavi and NavInfo occupied China pre-installed car navigation market with 55.1% and 42.8% share.
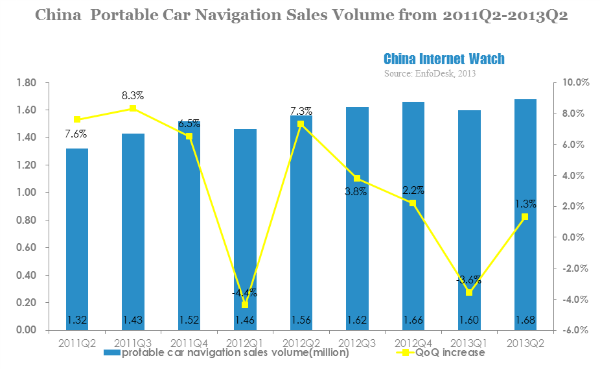
China portable car navigation sales reached 1.68 million in Q2 2013, 1.3% more than last quarter.
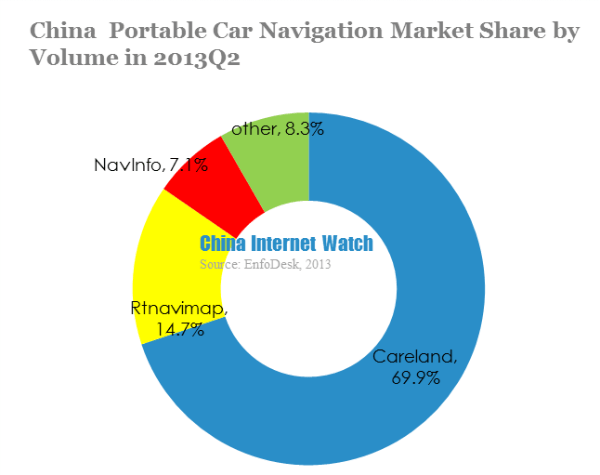
Careland topped with 69.9% in China pre-installed car navigation in Q2 2013, followed by Rtnavimap with 14.7%. NaviInfo ranked the third with 7.1% share.
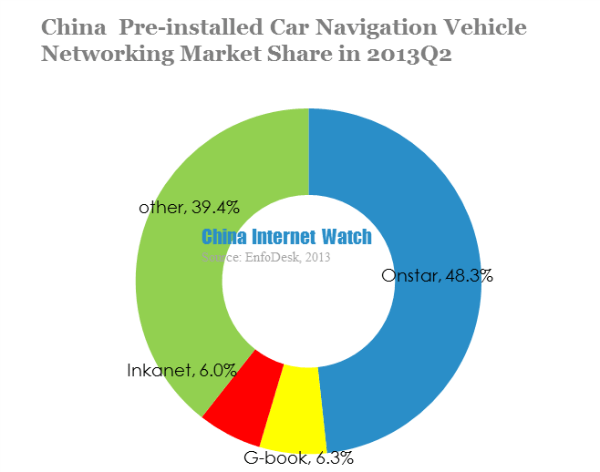
According to EnfoDesk, Onstar ranked the top in China pre-installed car navigation vehicle networking, with 48.3% market share. G-book and Inkanet ranked the second and third.
]]>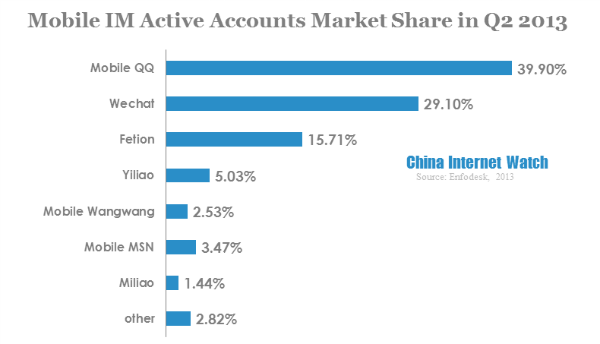
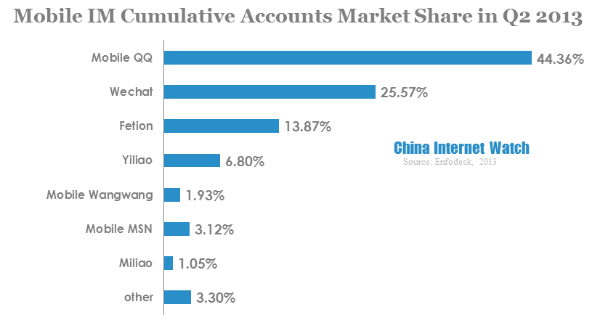
According to Enfodesk, in Q2 2013, Chinese cumulative mobile IM accounts hit 1.48 billion, with a QoQ increase of 21.3%. Chinese mobile IM active accounts reached 770 million, 75% more than that of 2012.
Mobile QQ was the top mobile IM app with 39.9% market share,, followed by Wechat with 29.1%. Together, QQ and Wechat occupied nearly 70% of mobile IM market.
Mobile IM app is a supplement for satisfying multi-device using experience, making communication as convenient as possible. Mobile QQ and Wechat incorporated game, SNS and media into its apps while strengthening communication function; China telecom newly launched Yiliao, gained its users fast by differentiate products basing on advantages of telecom operator and free service.
]]>
You must have a Baidu Stats account to use this service though you don’t necessarily have to install any code on the check you want to check loading performance with this tool.
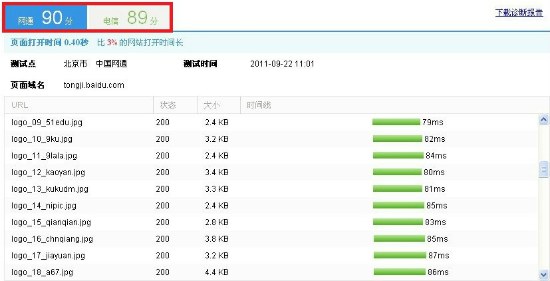
The test results show the page loading speed in seconds, compared with other sites. You will get an idea about the percentage of sites that are faster than yours.

This tool even provides recommendations on what you can do to improve the page loading speed.
]]>